Risk Factors Associated with Systemic Sclerosis Hospitalization Save
A retrospective study of systemic sclerosis patients shows that acute hospitalization and mortality were not uncommon and were often linked to SSc-related lung disease.
Record review of 95 SSc patients from a single-centre cohort seen between 2010 and 2020 found that over half (53 patients) required acute hospitalization, with a total of 164 admissions.
The most frequent causes for hospitalization:
- Infectious diseases (27%; 70% due to pneumoniae, of which 74% had SSc-associated ILD)
- Cardiac disease (16.5%)
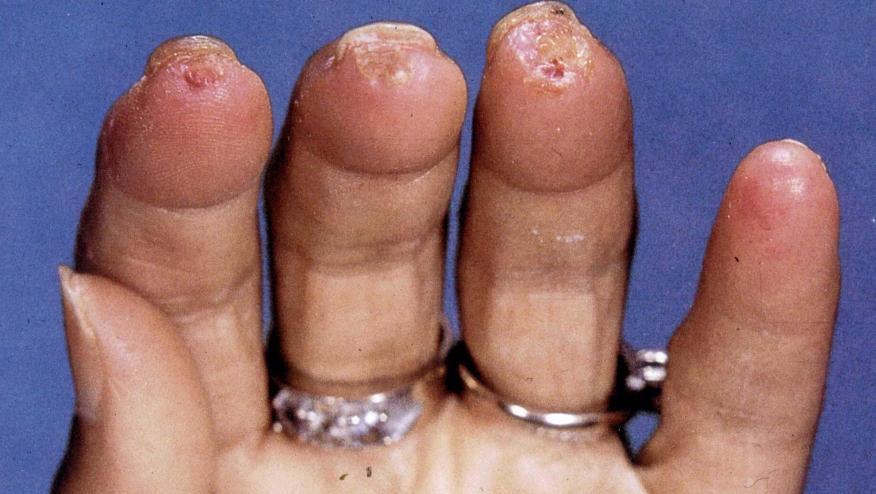
- Peripheral vascular disease and digital ulcers (12.8%)
- Pulmonary hypertension (PH) (9.8%)
- Interstitial lung disease (ILD - 9.1%).
In the first 5 years of followup, hospitalizations increased, driven by infection and cardiac admissions. But in the last 5 years there has been a decrease in ILD admissions.
The in-hospital mortality was 9% (14 patients) and the causes of death were:
- Pneumonia (36%)
- Heart failure (21%)
- Cancer (21%),
- PH (14%)
- ILD (7%).
Risk factors for both acute admissions and mortality, included: gender, race, digital ulcers, cardiac dysfunction, ILD and PH. Infection was the principal cause of acute hospitalization and mortality, mainly due to pneumonia. In multivariable analysis, only digital ulcers (OR 6.29) and diastolic LV dysfunction (OR 7.34) were associated acute hospital admission.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.