Genetic Analysis of Asymptomatic Antinuclear Antibody Positive Patients Save

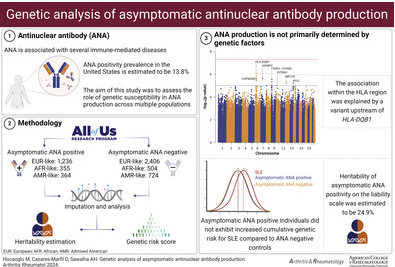
A large scale genomic population study found antinuclear antibodies (ANA) in up to 14% of the population; most with ANA are asymptomatic, and ANA production is not associated with significant genetic risk.
Asymptomatic individuals who were either ANA positive or ANA negative from the All of Us Research Program genomics were studied. A cumulative genetic risk score for lupus was constructed using previously reported genome‐wide significant loci.
The study included a total of 1,955 asymptomatic ANA positive and 3,634 asymptomatic ANA negative individuals. The multipopulation meta‐analysis revealed SNPs with a suggestive association (P <1 × 10−5) across 8 different loci, but no genome‐wide significant loci were identified.
The most significant gene association was a variant upstream of HLA‐DQB1, (rs17211748, P = 1.4 × 10−6, odds ratio 0.82, 95% confidence interval 0.76–0.89).
The heritability of asymptomatic ANA positivity was estimated to be 25%. Individuals.
Importantly, those who were asymptomatic and ANA positive did not exhibit increased cumulative genetic risk for lupus compared with individuals who were ANA negative.
ANA production is not associated with significant genetic risk and is primarily determined by environmental factors.









If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.