All News
Two Week Methotrexate Hold with COVID-19 Vaccination
A cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients evaluated immunogenicity of COVID vaccination with and without holding methotrexate (MTX) for and 2-weeks and showed better immunogenicity, but more RA flares with the second MTX withdrawal.
Read ArticleCOVID-19 Death is Dependent on Age and Type I IFN Autoantibodies
A study in PNAS of has shown that autoantibodies against type I interferons (IFNs) are strong predictors of death from COVID-19.
Read ArticleWhat Happened to Kawasaki Disease During COVID-19?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, a new COVID-related syndrome in children, the "Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children" (MIS), was described as being similar to but distinctly different than childhood Kawasaki's disease (KD). A new epidemiologic report shows that while MIS-C cases rose, KD cases fell and remained low during the period of masking and school closure.
Read ArticleFlares Not Increased Following Recombinant Zoster Vaccine Injections
Insurance claims analysis has shown that the use of the (CDC recommended) recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) for prevention of herpes zoster was highly used in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases and was safe, as higher rates of arthritis flares were not evident.
Read ArticleWhat do our lupus patients think about treat-to-target?
In SLE, two targets that are increasingly used are the DORIS 2021 Remission and the Lupus Low Disease Activity (LLDAS). T2T is more likely to be successful if the treating clinicians and the patients set the treatment goals together. What do our patients think about T2T and do they have any say/concern?
Read ArticleMMWR: Monkeypox Outbreak in Nine States
CDC is tracking multiple reported U.S. monkeypox cases, and monitoring cases in persons in countries without endemic monkeypox and with no known travel links to an endemic area; current epidemiology suggests person-to-person community spread.
Read ArticleAre TYK2 inhibitors ‘ticked’ to be part of the JAK family?
Are TYK2 inhibitors JAK inhibitors? Are they effective in PsA? Are they safer than JAKi? Read on to learn more.
Read ArticleRecommendations – Good & Bad (5.27.2022)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news, regulatory updates and journal reports from the past week on RheumNow.com. This week gout worries, mortality risks, measuring anti-drug antibodies and a better way in lupus?
Read ArticleIncreasing Corticosteroid Use in Non-Hospitalized COVID-19
JAMA reports that despite NIH recommendations (that corticosteroids only be used in hospitalized COVID-19 patients), nonhospitalized COVID infected patients were oftent prescribed systemic corticosteroids.
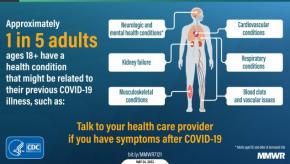
Read ArticleLong COVID Manifestations
The acute consequences of a SARS-CoV-2 infection may be bothersome or devastating, but the long-term consequences may lead to so-called "long COVID" syndrome. Long COVID appears to affect up to 20% of those who survive COVID-19 infection.
Read ArticleThe Inflammation Reflex (5.20.2022)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from the past week on RheumNow.com. This week, neuroimmunology leading to therapy, the cold shoulder approach and Regulatory updates from the FDA.
Read ArticleMethotrexate Monitoring (5.13.2022)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from the past week on RheumNow.com. Bad news for digitial ulcers in Systemic sclerosis, Readmissions in Lupus and Thrombocytopenia in APL patients.
Read ArticleWiki Guidelines Approach to Pyogenic Osteomyelitis
A crowd sourced, WikiGuidelines approach to clinical treatment guideline development for pyogenic osteomyelitis yielded 7 important clinical questions, 2 clear treatment recommendations and 5 topic reviews to inform future treatment or investigations.
Read Article$30 Billion and Counting (4.29.2022)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports and takes viewer questions this week.
Read ArticlePre-exposure Prophylaxis for COVID-19 (4.22.22)
Dr. Jack Cush discusses the news and recent journal reports from last weeks RheumNow.com, and answers viewer questions from #ACA - Ask Cush Anything.
Read ArticleCOVID-19 Vaccination Uptake and Perceptions in Rheumatic Patients
Putman et al has reported vaccine survey results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance (C19-GRA) in Lancet Rheumatology showing the uptake and vaccine hesitancy among people with rheumatic diseases (RMD).
Survey data from 7005 vaccinated and unvaccinated, adult RMD respondents from 102 countries was analyzed.
Evusheld as Protective Therapy in High Risk COVID-19 Patients
A single dose of the monoclonal-antibody AZD7442 (combination of tixagevimab and cilgavimab) has been shown to be safe and effective as prophylaxis against COVID-19 infection in high risk individuals who tested positive for COVID-19.
Read Article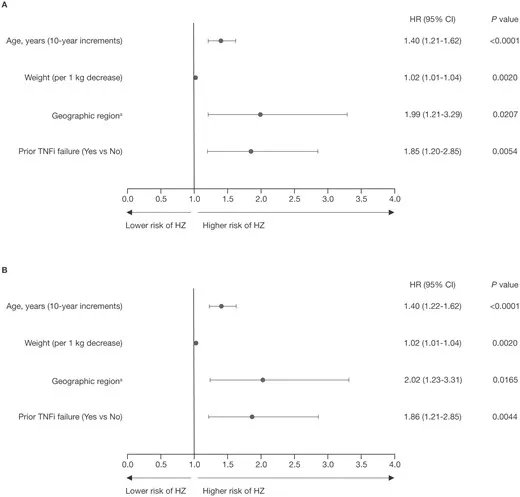
Links:
Links:
Links: