Quarterly Canakinumab Reduces Gout Risk Without Affecting Uric Acid Save
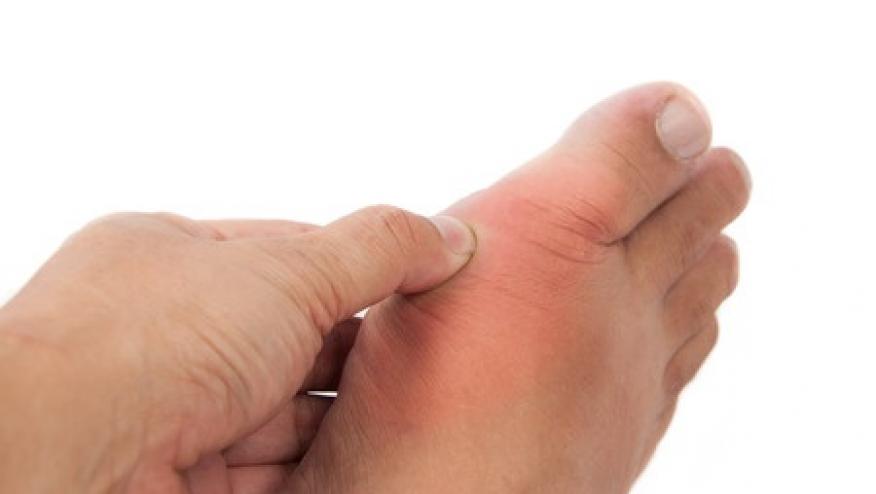
The Annals of Internal Medicine reports that interleukin-1 (IL-1) inhibitor treatment is associated with a reduced risk of gout attacks - such are the findings of an anlysis of the CANTOS study previously reported at the Annual ACR 2017 meeting in Washington, DC.
The CANTOS (Canakinumab Anti-inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study) study set out to assess whether antiinflammatory therapy, in the form of an IL-1 inhibitor canakinumab, could reduce risk of a future cardiovascular event in high risk individuals. The results were reported in 2017 in the Lancet and NEJM and showed that canakinumab, 150 mg every 3 months significantly lowered rate of recurrent cardiovascular events (independent of lipid-level lowering) and it also reduced total cancer deaths, especially lung cancer. These effects were dose dependent.
Solomon et al. now reports on the effects on quarterly canakinumab on serum uric acid (sUA) levels and gout attacks in the 10,059 patients enrolled with a history of prior myocardial infarction and an elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) level. Patients were followed for a median of 3.7 years.
Among placebo treated patients, the frequency of gout rose nearly 20 fold as sUA concentrations rose from 404.6 to 535.4 µmol/L or higher (gout risk rose from 0.28 to 5.94, respectively, per 100 person-years).
Receiving canakinumab was not associated with reductions in sUA over time but was associated with significantly reduced rates of gout attacks (hazard ratios ranged from 0.40 to 0.48). Thus IL-1 inhibition lead to a 50-60% reduction in gout attacks along with a significant drop in CRP levels, but no effect on sUA levels.
While these data and other studies showing the efficacy of IL-1 inhibition in treating acute gout are encouraging, the cost of biologic therapy to either treat or prevent gout makes such therapies impractical for most. Nonetheless, there may be benefits to targeting IL-1 and innate immunity in those at risk for gout.
Editors note: canakinumab is not FDA approved for use in gout. It is FDA approved for use in systemic JIA and Periodic Fever syndromes (CAPS, FMF, HIDS).









If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.