2023 ACR/EULAR Antiphospholipid Syndrome Classification Criteria Save
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and EULAR have combined efforts to establish an international multidisciplinary Steering Committee to develop classification criteria for the new antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) to be applied in observational studies and clinical trials.
A 24-member international Steering Committee, included APS experts and 3 patients who developed criteria in 4 phases: 1) Phase I, criteria generation by surveys and literature review; 2) Phase II, criteria reduction by modified Delphi and nominal group technique exercises; 3) Phase III, criteria definition, further reduction with the guidance of real-world patient scenarios, and weighting via consensus-based multicriteria decision analysis, and threshold identification; and 4) Phase IV, validation using independent adjudicators’ consensus as gold standard recommendations.
There are 3 takeaways from this effort:
1) The 2023 ACR/EULAR APS classification criteria require:
- An entry criterion of at least one positive antiphospholipid antibody (aPL) test within 3 years of an aPL-associated clinical criterion (from one of 6 domains)
- aPL tests include: a) lupus anticoagulant test, or moderate-to-high titers of b) anticardiolipin or c) anti-β2-glycoprotein-I antibodies [IgG or IgM]) within three years(b) of the clinical criterion
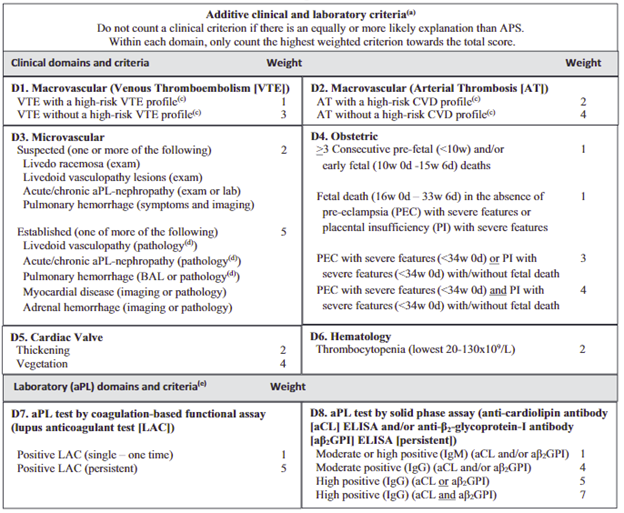
- Clinical Domain criterion: D1) macrovascular venous or D2) arterial thromboembolism, D3) microvascular disease (livedoid, aPL nephropathy, pulmonary hemorrhage), D4) Obstetric (fetal loss, preeclampsia, placental insufficiency), D5) Cardiac Valve thickening or vegetation, D6) Thrombocytopenia
2) An additive weighted criteria score (range 1–7 points each) from 6 clinical domains abnormalities (above) and 2 laboratory domains (aPL assay weighted scores).
3) Antiphospholipid Syndrome criteria is met if there are at least 3 points from clinical domains AND at least 3 points from laboratory domains.
The new APS criteria had a specificity of 99% and a sensitivity of 84% (compared to the 2006 revised Sapporo classification criteria 86%, and 99%, respectively).
These new ACR/EULAR APS classification criteria were established to be hierarchically clustered, weighted, and risk-stratified criteria reflect the current thinking about APS, providing high specificity and a strong foundation for future APS research.
Weighted Scoring










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.