Are Combination Biologics Safe? Save
Although package inserts commonly warn against combining the use of biologic or targeted therapies, there is growing interest in such combination therapy for patients with problematic immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID). Real-life data from a French observational study suggests the overall risk of severe adverse events (SAE) with combotherapy does not seem to be increased (vs monotherapy), but certain combinations warrant caution.
Multicenter observational study of IMID patients under combotherapy compared outcomes to a matched monotherapy control group. Combotherapy included different biological and targeted synthetic DMARDs. The primary endpoint was the occurrence of serious adverse events (SAE), defined by severe infections, major cardiovascular events, neoplasia and mortality (all-cause).
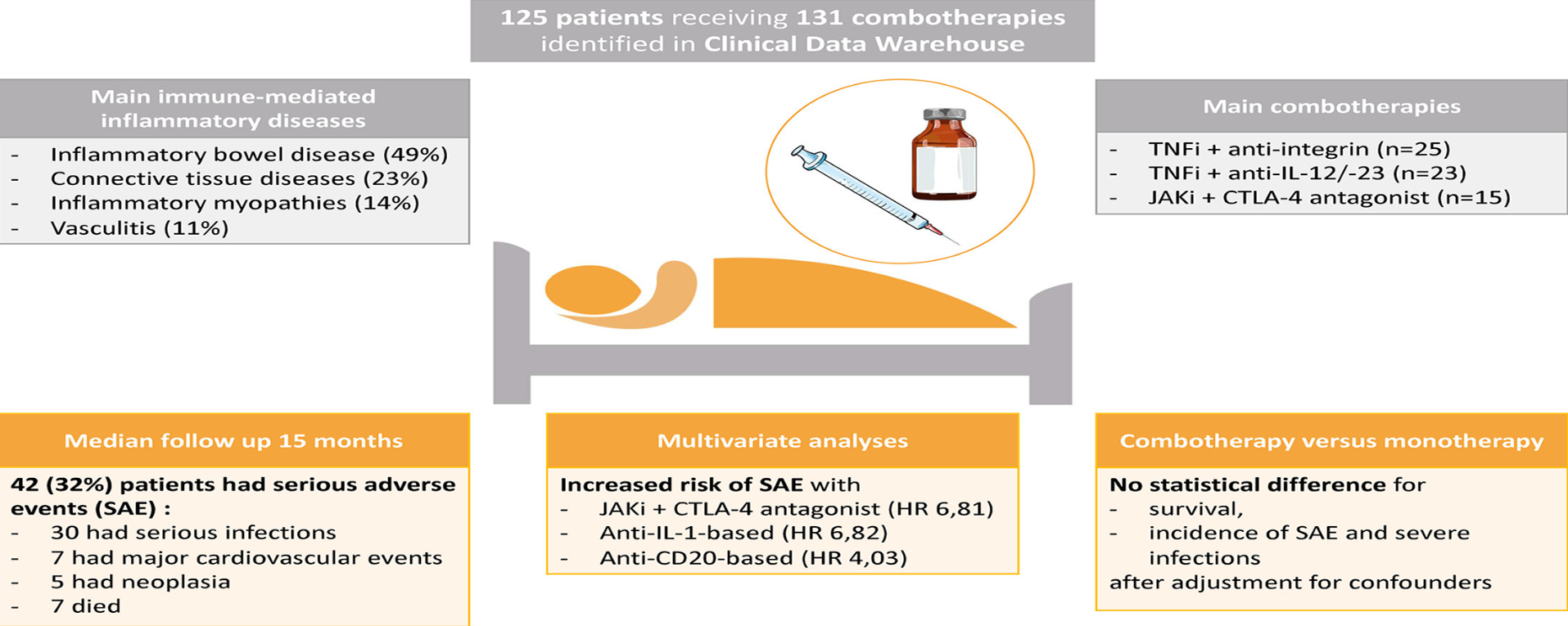
Among a total of 42,071 IMID patients they identified 131 combotherapy lines among 125 patients (median age of 36 years, 58 % females), treated between 2017 and 2022. Most frequent IMIDs were inflammatory bowel disease (49%), connective tissue diseases (23%), inflammatory myopathies (14%) and vasculitis (11 %).
With a median follow-up of 15 months, 30 (24 %) patients presented severe infections, 5 (4 %) neoplasia, 4 (3.2 %) venous thromboembolism, 3 (2.4 %) acute coronary syndromes and 7 (5.6 %) deaths. The 1-year cumulative incidence of SAE and severe infections were 29 % and 24 %, respectively.
The survival, incidence of SAE and severe infections were not statistically different between combotherapy and monotherapy controls (n=251) after adjustment for confounders.
However, In multivariate analyses, higher SAE rates were seen with the following combotherapies:
- abatacept + JAKi (HR 6.81, 95 %CI 1.88–24.68)
- anti-IL-1-based (HR 4.82, 95 %CI 1.17–19.89)
- anti-CD20-based (HR 4.03, 95 %CI 1.22–13.31)
It should be noted that these are observations and not reliable given the biases of inclusion. While the risk of SAE under combotherapy does not appear to be greater that monotherapy in this study, certain combinations yielded significantly higher SAE rates, therefore warranting caution.
Join The Discussion
Interesting, but what about the efficacy?
Disclosures
The author has no conflicts of interest to disclose related to this subject










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.