New Onset Rheumatic Disorders with COVID-19 Infection Save
The journal Cells has published a review of new rheumatic disorders following COVID-19 infection. Rheumatologists have infrequently noted such events and wondered what is the true incidence or range of possible manifestations.
Infection can be an infrequent trigger to immune dysregulation and subsequent autoimmune phenomena, that could range from autoantibody production, hyperinflammation, vascular events or even specific systemic and rheumatic autoimmune diseases.
This review reports the results of a systematic review of reports from December 2019 to September 2021.
A total of 99 patients (fulfilling classification criteria) for a specific rheumatic autoimmune disease were identified. This included cases of vasculitis, inflammatory arthritis, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), sarcoidosis, and isolated cases of systemic sclerosis and adult-onset Still’s disease.
Whether there is true linkage between COVID-19 and these rheumatic diseases cannot be surmised from this review that largely describe the scope of associated (causal or casual) events.
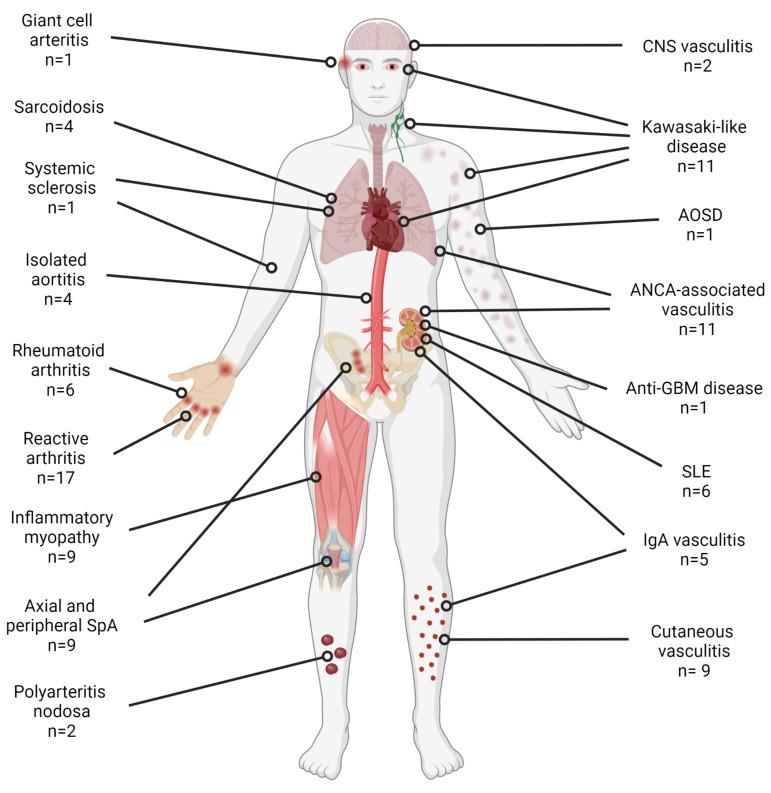
The report included cases of:
- Vasculitis: there were 46 cases from 43 articles that fulfilled criteria and/or nomenclature for immune-mediated vasculitides. Many cases were excluded for incomplete data, no objective vasculitis, or not meeting established criteria. The vasculitis usually involved the skin in (60.8%), kidney (30.4%), eyes (21.7%), lymph nodes and heart (19.6% each), lungs (15.2%), joints (13%), aorta (10.8%), gastrointestinal tract (8.7%), (6.6%), ENT region and the brain (4.3%). Single organ vasculitis was seen in 15 cases and 31 had systemic vasculitides. Most were (60.8%) small-vessel vasculitis, but medium-vessel (28.3%) and large-vessel vasculitides (10.8%) were seen. The systemic vasculitides included Kawasaki disease in 11, AAV in 11, IgA vasculitis in 5, PAN in 2, and giant cell arteritis (GCA) and anti-GBM disease in 1 each.
- Arthritis: They found 28 studies that described 6 patients with RA, 3 with axial SpA, 6 peripheral SpA and the remaining 17 patients had isolated arthritis in the context of post-COVID-19.and did not fulfill the classification criteria for RA or SpA.
- Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: There were 9 cases from 8 articles were included. Six cases fulfilled classification criteria for adult and juvenile IIM and 3 patients were classified as possible polymyositis. ANA positivity was seen in 3 cases, 2 with anti-SAE1 antibody, 2 with anti-Ku antibodies and one each positive for anti-MI 2b, anti-Ro/SSA antibodies, anti-Smith antibody and MDA-5.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: only 6 cases of COVID associated SLE were found (4 women). Manifestations of lupus included proteinuria (5), acute renal injury (3) and hematological (thrombocytopenia (6), leukopenia (1)) in all cases, serosal involvement in 4 cases, (pleural effusion (3), pericardial effusion (2), ascites (1)) and cutaneous in 3 cases.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.